When you’re pregnant, what you eat isn’t just about you anymore—it’s about nourishing your little one too. This makes getting all the right nutrients through a well-balanced pregnancy diet most essential. Every bite you take is helping build those tiny bones, organs, and all-important neural tube. Plus, it’s keeping you in top shape too, which is key for a smooth ride through pregnancy.
This article has got the lowdown on all the essential nutrients for a healthy pregnancy. From what to eat and what not to eat, we’ve covered everything you need to know for a healthy journey through this transformative phase.
Importance of Nutrition During Pregnancy
Firstly, why should you prioritize a pregnancy diet? This is because when you’re pregnant, your body undergoes significant changes and a little one depends on you for all their growth needs. So, it’s vital to nourish yourself properly.
Before pregnancy, maybe you could get by with your usual meals, not worrying too much about every little nutrient. But once your little one is on board, you’ll need other necessary nutrients like folic acid to keep both you and your baby thriving.
Key reasons why you should focus on preparing healthy meals for pregnancy are:
- Nutrient demand: The developing baby requires a variety of nutrients such as folic acid, iron, and calcium for proper growth and development.
- Maternal health: Nutrient-rich diet supports your health, energy levels, and overall well-being.
- Organ development: Essential nutrients contribute to the formation of the baby’s vital organs.
- Preventing deficiencies: A balanced diet helps ensure you’re both getting everything you need, avoiding any hiccups along the way.
- Immune support: Proper nutrition boosts the immune system, necessary for both, to fight infections and illnesses effectively.
- Energy requirements: Pregnancy demands increased energy, and a nutritious pregnancy diet plan ensures a sufficient supply for both of you.
Essential Nutrients for a Healthy Pregnancy (+ Food Sources)
Now that we’ve covered the importance of nutrition during pregnancy, let’s explore essential nutrients during pregnancy. This list makes sure you’re stocked up on all the necessary nutrient sources.
1. Folic Acid
Let’s talk about folic acid—one of the most essential nutrients during the pregnancy phase. It prevents neural tube defects and other birth abnormalities in your little one. Plus, it’s not just about the baby; it’s got perks for you too, like reducing the risk of anemia and helping out with the placenta development.
Healthcare experts suggest keeping folic acid levels up even before you start trying for a baby. Why? Because the neural tube starts forming super early, often before you even realize you’re pregnant!
You can get sufficient folic acid through dietary sources like leafy green vegetables (Spinach, Kale), citrus fruits, beans, fortified cereals, lentils, legumes, and avocados. And if you need an extra boost, supplements are always an option—just take advice from your doctor first.
2. Iron
Consuming iron during pregnancy is essential to prevent iron deficiency anemia, ensure proper oxygen transport to the developing fetus, and support overall maternal and fetal well-being.
Include iron-rich foods like lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, lentils, fortified cereals, and leafy green vegetables into your pregnancy diet. Complement this with healthcare professional-recommended supplements to meet the increased iron demands during this phase.
3. Calcium
When you’re pregnant, you might be advised to include dairy products, leafy green vegetables, tofu, and fortified plant-based milk alternatives in your pregnancy diet. This is to ensure an ample intake of calcium, important for – the proper development of your baby’s bones, teeth, heart, nerves, and muscles. Plus, it’s got some nifty blood clotting abilities too, which is always a bonus during pregnancy!
Adequate calcium during the last trimester is particularly crucial as your baby’s growth peaks during this time. Getting enough calcium also reduces the risk of preterm birth, hypertension, and preeclampsia—a condition with some serious blood pressure complications.
4. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are necessary for a healthy gestation period, supporting the development of the baby’s fetal brain and retina. They also enhance cognitive development, potentially reducing the risk of preterm birth.
Omega-3s also reduce inflammation, keep you feeling good, and support your heart health during pregnancy.
Sources of omega-3 fatty acids include fatty fish (such as salmon, mackerel, and trout), walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds. If fish isn’t your thing – supplements prescribed by healthcare professionals can help ensure an adequate intake of this essential nutrient during pregnancy.
5. Protein
One of the most essential nutrients during pregnancy for a lot of reasons. Your growing baby, placenta, and your own body all rely on protein for growth, development, and staying healthy. Adding protein to your pregnancy diet is key for building your baby’s organs, muscles, and tissues. Plus, it supports the increased blood volume in you and aids in the synthesis of enzymes and hormones.
Protein-rich food sources include lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, tofu, and nuts. Adding these to your diet plan means you’re getting all the essential amino acids needed for both you and your baby’s well-being during pregnancy.
6. Vitamin D
During pregnancy, your body relies on vitamin D to help absorb calcium, which is crucial for your baby’s bone and teeth development. Having sufficient vitamin D levels also boosts your immune system, keeping both you and your growing baby healthy.
If you’re not getting enough vitamin D, it can lead to a deficiency, which might mean trouble for your baby’s bone development, a weaker immune system, and a higher chance of pregnancy complications. Definitely an essential nutrient to keep an eye on!
You can find Vitamin D in food sources like fatty fish (salmon and mackerel), fortified dairy and plant-based milk, eggs, fortified yogurt, fortified tofu, and certain fortified cereals like oatmeal and bran flakes.
7. Iodine
Iodine is an essential nutrient during pregnancy as it regulates thyroid function, which is significant for metabolism and energy regulation. But that’s not all—it’s also super important for your baby’s brain and nervous system development. Ensuring you’re consuming enough iodine helps prevent any issues related to deficiency and ensures your little one grows strong and healthy from the get-go.
Iodine can be sourced from foods like seafood (fish, shrimp, seaweed), dairy products (milk, yogurt, cheese), eggs, and iodized salt.
8. Vitamin C
Your body relies on it to support the immune system, help absorb iron, and promote the growth of your baby’s bones and connective tissues.
A few vitamin C-rich food sources to include in your pregnancy meal plan are – citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruits), strawberries, kiwi, bell peppers, broccoli, tomatoes, and spinach.
9. Zinc
Zinc is a must-have nutrient for a healthy pregnancy because it supports fetal development, keeps your immune system strong, helps with DNA synthesis, ensures proper enzyme function, and works to prevent birth defects.
To obtain sufficient zinc during pregnancy, include dietary sources rich in zinc, such as lean meats (beef, pork, lamb), poultry (chicken, turkey), seafood (oysters, crab, lobster), dairy products (milk, yogurt, cheese), legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas), nuts and seeds (pumpkin seeds, cashews), whole grains (wheat germ, quinoa).
10. Vitamin A
Vitamin A is vital for fetal development, visual health, and a strong immune system. This vitamin is also known to support cell differentiation (specialization of cells for specific functions), and the production of healthy skin cells, aiding the body’s defence against infections.
While vitamin A is essential, it’s important to be mindful of how much you’re getting, especially from supplements containing retinol, during pregnancy. Too much can actually do more harm than good and may lead to birth defects. That said, you can still get your dose of vitamin A in a balanced way through natural food sources like:
- Colourful vegetables: Carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, kale, and broccoli.
- Fruits: Mangoes, apricots, and cantaloupe.
- Dairy products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt.
- Protein sources: Eggs and liver (in moderation).
11. Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6, also known as pyridoxine helps build your baby’s nervous system, including the neural tube. But, there’s more! B6 also helps with the production of red blood cells, prevents anemia, and keeps your energy levels up.
Some studies even say it can help ease morning sickness—talk about a win-win! So, it’s definitely on the essential nutrients during pregnancy list, right?
Including sources like lean meats, fish, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, and fortified cereals in the pregnancy diet ensures sufficient Vitamin B6 intake.
12. Vitamin B12
Having a baby growing within you means you need plenty of vitamin B12 to make sure everything’s developing just right. It’s a must-have nutrient for your baby’s nervous system, brain, and red blood cell development.
To ensure sufficient intake of Vitamin B12, include these items in your pregnancy meal plan – Lean meats (beef, chicken, turkey), fish (salmon, trout, tuna), dairy products (milk, yogurt, cheese), eggs, fortified cereals, fortified plant-based milk (such as almond or soy milk), and shellfish (clams, mussels).
13. Vitamin E
Adding vitamin E to your pregnancy diet chart offers antioxidant protection, boosts the immune system, and helps keep your cells healthy. Ample intake of it can even contribute to preventing certain complications like pre-eclampsia.
Vitamin E-rich food sources are almonds, sunflower seeds, spinach, broccoli, vegetable oils (sunflower, safflower, wheat germ), nuts (hazelnuts, pine nuts), and fortified cereals.
14. Magnesium
This mineral makes for a healthy pregnancy for several reasons. Magnesium supports muscle and nerve function, keeps your blood sugar in check, and even plays a role in bone development. And get this—it’s super important for your baby’s bones and teeth too, and helps keep your blood pressure in check. Appropriate magnesium intake can even help prevent complications like preeclampsia.
Food sources you can incorporate in your pregnancy diet to meet magnesium requirements during pregnancy are – leafy green vegetables (spinach, kale, Swiss chard), nuts and seeds (almonds, sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds), whole grains (brown rice, quinoa, whole wheat), legumes (black beans, chickpeas, lentils), dairy products (yogurt, milk), fish (salmon, mackerel), and avocado.
15. Fiber
Including fibre in your pregnancy diet is like giving your digestive system a boost in the right direction. It promotes regular bowel movements, preventing common issues like constipation. Fibre adds some extra bulk to your stool, making it softer and ensuring you have a healthy digestive system. And let’s be real—anything that helps ease pregnancy’s digestive woes is a win-win!
Plus, a fibre-rich diet does wonders for your overall gastrointestinal health, keeping things running smoothly and helping regulate blood sugar levels.
Fibre-rich food sources include whole grains such as oats, quinoa, and brown rice, legumes like beans and lentils, fruits such as berries and apples, vegetables like broccoli and spinach, nuts and seeds, and whole-grain cereals.
Insufficient nutrient intake may lead to your baby drawing them from your body, potentially affecting your long-term health. Therefore, you must include these nutrients in your pregnancy meal plan for both maternal and foetal well-being.
Pregnancy Diet Plan for All Trimesters
Here’s a breakdown of nutrient focus for each trimester during pregnancy:
Pregnancy diet chart for the first trimester
First trimester — the time when all the excitement begins! Those initial 12 weeks are like the building blocks for your baby’s growth, with key structures like the neural tube taking shape. That’s why focusing on nutrients like folic acid, iron, and vitamin B6 is crucial—they lay the groundwork for your baby’s development and even help ease the nausea spells. But, your body’s still going to need a variety of other nutrients like calcium, healthy fats, proteins, and plenty of fluids to keep things going smoothly.
Here’s a basic chart you can follow to ensure a well-rounded pregnancy diet.

Pregnancy diet chart for the second trimester
The second trimester, spanning from weeks 13 to 27, is the phase marked by an energy boost and development. It’s when your baby really starts to grow, with bones and teeth taking shape, organs and tissues developing, and cognitive and visual capabilities advancing.
To fuel all this amazing growth, it’s crucial to focus on key nutrients like calcium for strong bones, protein for tissue growth, and omega-3 fatty acids for brain and vision development. Check out this second-trimester diet chart for optimal nutrition and healthy pregnancy.
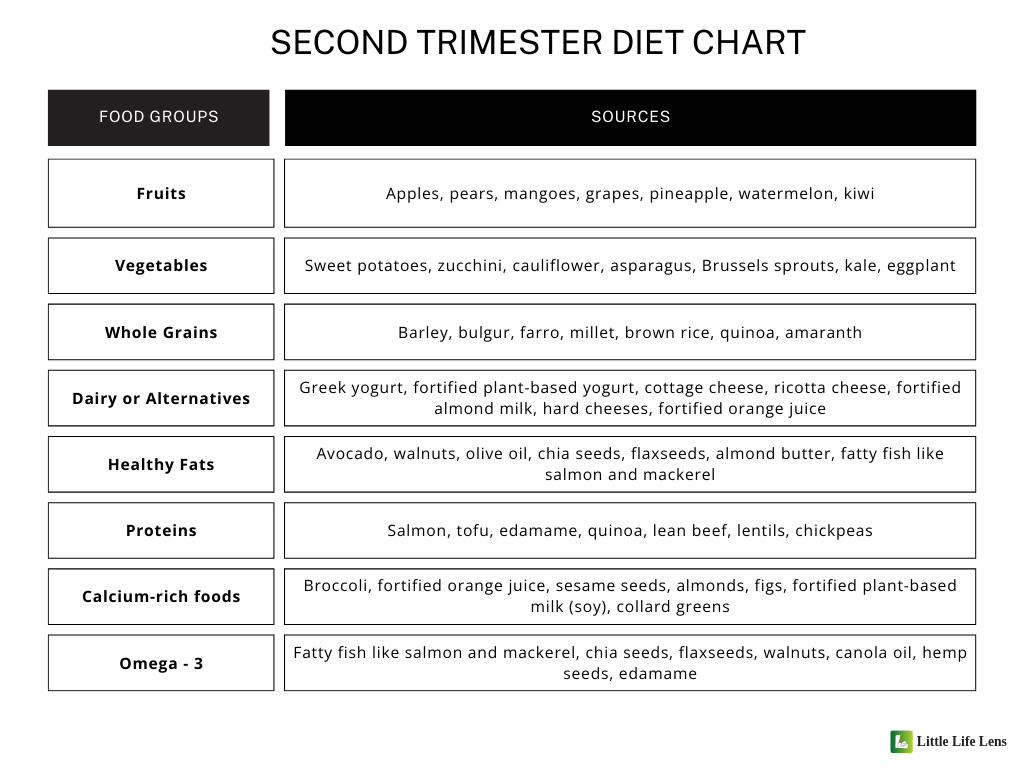
Pregnancy diet chart for the third trimester
The third trimester (Weeks 28-40) involves exponential growth in your baby’s development. During this pregnancy phase, the baby experiences extensive growth, refining organ functions, maturing the respiratory and nervous systems, and gaining substantial weight. This stage marks the final preparation for birth, emphasizing the importance of essential nutrients for pregnancy to ensure the baby’s health and readiness for delivery.

Note: While all nutrients are important throughout pregnancy, the emphasis on certain ones may shift based on the specific needs of both you and your baby during different stages of development. You must maintain a well-balanced diet and consult healthcare professionals for personalized guidance.
Daily Meal Plan for Expectant Moms
Here’s a sample daily meal plan designed to provide all the essential nutrients needed during pregnancy. Remember, you can always adjust it to fit your personal preferences, dietary requirements, and any recommendations from your healthcare provider.

What Not to Eat When Pregnant
During pregnancy, it’s important to be mindful of your food choices to ensure the health and well-being of both you and your baby. Here’s a list of foods to avoid or limit during pregnancy:
- Raw or undercooked seafood: High risk of contamination with harmful bacteria or parasites.
- Raw or undercooked eggs: Risk of salmonella infection.
- Unpasteurized dairy products: May contain harmful bacteria like Listeria or E. coli.
- Soft cheeses (e.g., Brie, Camembert, Feta): These cheeses may harbour Listeria.
- Excessive caffeine: Limit caffeine intake to reduce the risk of miscarriage; opt for decaffeinated versions.
- High-mercury fish (e.g., Shark, Swordfish, King Mackerel): May harm the baby’s developing nervous system.
- Alcohol: Consumption may lead to developmental issues and birth defects.
- Unwashed produce: Rinse fruits and vegetables thoroughly to remove potential contaminants.
- Artificial sweeteners (e.g., Saccharin): Some may pose risks; consult with a healthcare professional.
- Raw shellfish (e.g., Oysters, Clams): Risk of bacterial contamination.
- Uncooked or undercooked meats: May harbor harmful bacteria; ensure proper cooking.
6 Tips for a Nourishing Pregnancy Journey
While following a pregnancy diet, here are five essential tips to ensure a healthy gestational phase:
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water to support increased blood volume and overall well-being.
- Exercise regularly: Engage in approved exercises like walking or prenatal yoga for physical well-being.
- Rest well: Listen to your body, prioritize rest, and ensure sufficient sleep for both you and your baby.
- Manage weight gain: Consult with your healthcare provider to ensure healthy weight gain throughout pregnancy.
- Practice mindful eating: Practice mindful eating to savour meals and maintain a positive relationship with food.
- Go for regular check-ups: Attend regular prenatal check-ups to monitor pregnancy progress and address any concerns.
Just a heads up – everyone’s body is different so It’s good to consult your healthcare expert and get advice tailored just for you. They’ll consider things like your health, which trimester you’re in, and anything else unique to your situation. It’s all about making sure you’re getting the best support possible.




